
Treasury shares can always be reissued back to stockholders for purchase when companies need to raise more capital. If a company doesn’t wish to hang on to the shares for future financing, it can choose to retire the shares. Retained earnings are a company’s net income from operations and other business activities retained by the company as additional equity capital. They represent returns on total stockholders’ equity reinvested back into the company.

The “book value” of a company’s equity less all liabilities is its shareholders’ equity. It stands for an accounting value that is distinct from the market value or actual value of a corporation. The fundamental accounting equation is the quickest and easiest way to determine shareholders’ equity.
What Is Shareholder Equity (SE)?
In our modeling exercise, we’ll forecast the shareholders’ equity balance of a hypothetical company for fiscal years 2021 and 2022. Otherwise, an alternative approach to calculating shareholders’ equity is to add up the following line items, which we’ll explain in more detail soon. Under a hypothetical liquidation scenario in which all liabilities are https://www.bookstime.com/ cleared off its books, the residual value that remains reflects the concept of shareholders equity. Shareholders’ equity is the residual claims on the company’s assets belonging to the company’s owners once all liabilities have been paid down. Treasury stocks are repurchased shares of the company that are held for potential resale to investors.
While the data and analysis Stash uses from third party sources is believed to be reliable, Stash does not guarantee the accuracy of such information. Nothing in this article should be considered as a solicitation or offer, or recommendation, to buy or sell any particular security or investment stockholders equity formula product or to engage in any investment strategy. No part of this material may be reproduced in any form, or referred to in any other publication, without express written permission. Stash does not provide personalized financial planning to investors, such as estate, tax, or retirement planning.
What are the Components of Shareholders Equity?
The shareholders equity ratio, or “equity ratio”, is a method to ensure the amount of leverage used to fund the operations of a company is reasonable. Next, the “Retained Earnings” are the accumulated net profits (i.e. the “bottom line”) that the company holds onto as opposed to paying dividends to shareholders. Often referred to as paid-in capital, the “Common Stock” line item on the balance sheet consists of all contributions made by the company’s equity shareholders. Current assets are those that can be converted to cash within a year, such as accounts receivable and inventory. Long-term assets are those that cannot be converted to cash or consumed within a year, such as real estate properties, manufacturing plants, equipment, and intangible items like patents. These earnings, reported as part of the income statement, accumulate and grow larger over time.
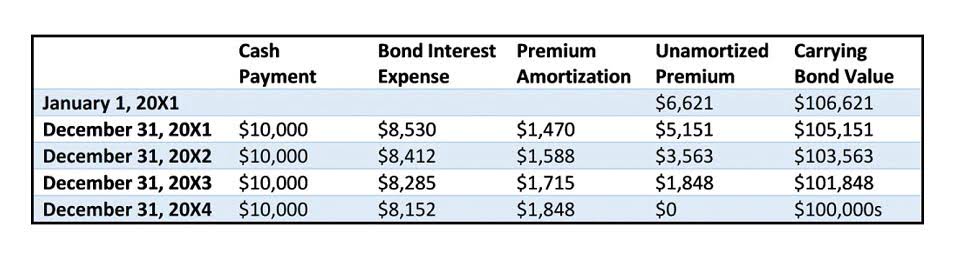
Over time, the company’s shares will change in value; the company may also issue more shares or buy some back from investors. All these things affect stockholders’ equity, as do the assets and liabilities a company accrues over time. Investors and financial analysts use shareholders’ equity as one way to assess a company’s financial situation. Usually, if the number is positive, the company can afford to pay off its liabilities, while a negative number could indicate financial trouble. Keep in mind that book value alone is not a definitive indicator of fiscal health, and it should be considered along with the company’s overall balance sheet, cash flow statement, and income statement. Stockholders’ equity is the remaining assets available to shareholders after all liabilities are paid.